Robotics in Warehouse Automation is changing the Fulfillment Paradigm
This article explores the benefits of robotics and automation in the warehouse industry and how it's shaping the fulfill...


The warehouse industry is undergoing a transformation, as the need for more efficient and automated systems becomes increasingly important. This rapid adoption of robotics and automation is to replace outdated procedures and infrastructure due to labor scarcity and growing demand for staffing. According to MHI's 2022 report, automation, and robotics usage is expected to grow from 28% to 79% in five years. Robots can be customized for specific processes, so it's important to assess current bottlenecks before introducing them. Organizations are looking to adopt flexible and scalable robotic solutions for their distribution facilities. The same survey found that 79% of companies are currently using or plan to use AMRs for order picking. This article explores the benefits of robotics and automation in the warehouse industry and how it's shaping the fulfillment paradigm.
Robotics alleviate fulfillment-related pain points
Robotics in warehouses can help alleviate fulfillment-related pain points by increasing efficiency and productivity, reducing errors, and optimizing storage. Speaking for Quicktron Robotics, our robots help workers and companies to be more efficient and productive—to the tune of a 3x - 4x increase in picking efficiency, operators can pick 200,000 order lines/day. Collision-free path planning ensures worker safety, storage optimization, robot collaboration, and other algorithms ensure fast delivery of goods to the operator and multiple orders can be fulfilled simultaneously which boosts the efficiency of picking, replenishment, returns processing, and other processes by 2-3 times.
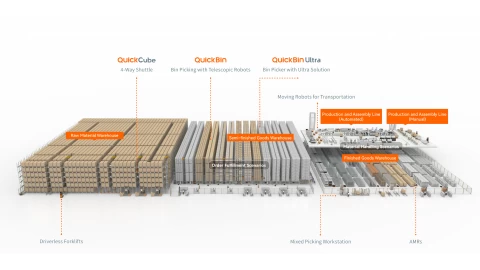
Human Robot Collaboration in an Automated Warehouse
The majority of mobile robots are deployed in warehouses for order picking. Goods-to-person is one of the dominating technologies today. The main advantage is time-saving and productivity setting humans free from the tedious tasks of moving things around. Based on different research, pickers in medium to big warehouses frequently walk five to eight miles per day. Travel time accounts for around 75% of their total time.

In an automated warehouse, robots do the traveling between zones while employees remain stationary at workstations. With Quicktron's goods-to-person technologies, all the goods moving to/from the workstations or conveyors is been done by AMRs. Picking rates can reach up to 200,000 order lines per day in the most productive conditions, and can easily double compared to manual processes. This is the type of increased efficiency that drives these types of decisions.
By autonomously delivering goods to a fixed picking station, "goods-to-person" solutions get rid of numerous wasteful activities in the warehouses. The use of AMRs brings the revolution in order picking. Advanced warehouse management systems help increase picking efficiency by drastically reducing picking errors. The combination of advanced algorithms, sensors, and technologies like QR code, and LIDAR in robots that can move around in warehouses avoiding obstacles, delivering goods, and even getting to recharge stations to recharge themselves while low batteries made a revolution in intralogistics.
Quicktron's robotic solutions altering the fulfillment paradigm!
Quicktron Robotics offers modular and flexible solutions for warehouse automation. Its shelf/rack-to-person and Quickbin technologies utilize AMRs to deliver goods to workstations, increasing productivity and reducing errors. By analyzing order history and optimizing storage, Quicktron can handle order peaks and improve overall picking efficiency. Customers who have deployed Quicktron's solutions have experienced a significant reduction in training expenses while doubling worker productivity and improving order-picking accuracy. With their adaptability and reconfigurability, Quicktron's solutions can be tailored to meet the specific needs of any warehouse, making it an ideal choice for businesses across retail, wholesale, and e-commerce channels.
By deploying these systems, customers have lowered training expenses by up to 80% while doubling worker productivity. Quicktron's technology eliminates the need for additional workers even during peak periods, significantly improving order-picking accuracy.
For example, Cainiao, Alibaba's logistics arm, has established a global network ensuring 24-hour delivery in China and 72 hours globally. To optimize its processing rate, Cainiao automated its main warehouse with Quicktron shelf-to-person solutions, which stores products for Tmall, one of the largest online shopping platforms in terms of inventory. The Quicktron system with different zonings of products and picking methods helped improve warehouse performance and altered China's order fulfillment paradigm.

Recently, Winit deployed Quickbin technology to organize and densely store over 80,000 bins, which are delivered to and from workstations by 180+ QuickBin robots, enabling smooth fulfillment of orders by fine-tuning inbound/outbound processes and reducing cost significantly. Quickbin is a popular solution from Quicktron, capable of handling the dispatch of goods from various cross-border online sellers.

These solutions are adaptable to processing numerous orders across retail, wholesale, and e-commerce channels. By analyzing order history, Quicktron's dynamic storage predicts future demand to determine the optimal location for shelves and bins, shortening the distance to the workstation and enhancing picking efficiency. The combination of high-density automated storage systems with goods-to-person picking has introduced unprecedented efficiency to distribution, particularly e-commerce fulfillment.

Arslan crafts compelling content, executes social media campaigns, and masters online ads, webinars, podcasts, and copywriting. He builds strong relationships with clients, empowering them with support and resources to achieve their sales goals. Leveraging data insights, he refines strategies and collaborates seamlessly to stay ahead of the digital curve.